Pupillometry Explanation
Pupillometry is the measurement of the pupil diameter and reactivity (changes in pupil size). It is conducted using a Pupillometer being a device that measures the size of the pupil and its reactions to various stimuli.
Pupillometry provides insights into a variety of physiological, psychological, and neurological states and is considered an accurate indicator of Autonomic Nervous System function.
We use ‘Ocula’ which measures both eyes simultaneously. We have been a significant contributor to the development of this technology.
This method of testing is quick (17secs), easy and accurate. Which makes it lend itself to repeatedly monitoring progress, especially of the symptoms pertaining to the Autonomic Nervous System.
Pupillometry helps in diagnosing and monitoring neurological disorders, such as brain injuries, cerebral diseases, and other conditions that affect the nervous system.
The primary measurements include pupil size (diameter), reaction time to light (how quickly the pupil constricts in response to light and dilates again in its absence), and the rates of these changes.
Digital pupillometry provides objective data that can complement other diagnostic procedures.
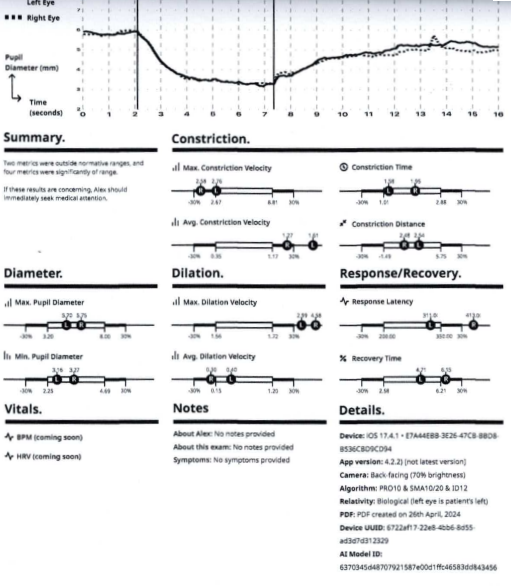
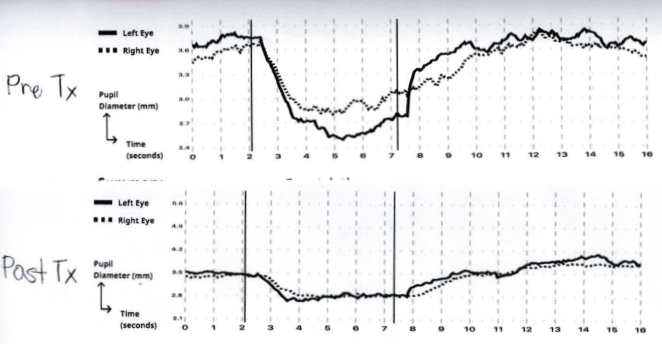
Below is a typical graphical representation of the report the application generates and beneath that is just the graphical part of reports before and after treatment of a patient that presented with Post Concussion Syndrome.
A bit more detail.
The ability to precisely control the size of the pupil is to regulate the intensity of light reaching the Retina.
The photosensitive chemicals within the rods and cones of the retina along with theW3 / object-motion retinal ganglion cells have a natural exhaustion point. The greater the intensity of light the sooner these cellular photo-chemical reactions will exhaust. Optimal visual acuity will occur with the greatest level of photochemical activity which leads to nerve conduction into the Optic Nerve and Brain. To regulate the amount of light to be within an intensity range that the cellular metabolism can accommodate is to acquire the greatest information from the visual scene.
The more detail we can see, the better will be our voluntary and reflexive reactions to the environment.
As the photosensitive chemical reactions within the retinal cells are quickly exhausted the eye undergoes micro saccades ie, the eyeball is rapidly 'jiggled’, at a microscopic level, so that the stream of photons (Light) will move from one cell onto those adjoining it, giving all the cells time to replenish.
The pupil is constricted by the Parasympathetic part of the Autonomic Nervous System(ANS). Pupillary dilation is initiated and maintained by the sympathetic part of the Autonomic Nervous System.
So when we are alert, our pupil will be big, allowing plenty of detail of our environment to be seen. The parasympathetic system of the ANS will control that to keep the light level within the physiological range.
A bright light will automatically make the parasympathetic system constrict the pupil. In less than a second there should be maximum constriction and the parasympathetic system should hold the pupil constricted.
This is called the Pupillary Light Reflex.
When there is an imbalance between the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic systems there will be aberrant reactions to the bright light.
Dysautonomia is a descriptive term for a dysfunction within the Autonomic Nervous System. The commonest dysfunction is that of an overstimulated sympathetic component of the ANS. This typically looks like a ‘fight or flight’ reaction, at the very least a hyper alert state. This hyper alert state is kept in check by the parasympathetic component of the ANS. The Parasympathetic component tends to ‘rest and recover’ or ‘heal and digest’.
Pupillometry gives an indication as to the balance of the Sympathetic Versus Parasympathetic systems.
Normal physiology suggests the initial pupillary constriction should occur rapidly and hold at the constricted level for the remainder of the test period.
A slow response time is abnormal. The inability to hold the pupil constricted is also abnormal.
A reduced parasympathetic response can slow the pupillary constriction response time while a hyperactive sympathetic system will prevent the pupils from staying constricted.
Concussion and Ocula Notes - These are rough notes created for an in-house presentation.
TBI is a growing public health concern, affecting more than 1.7 million Americans at an estimated annual cost of $76.5 billion dollars. It is a leading cause of death and disability for children and young adults in industrialised countries, and people who experience TBI are more likely to develop severe, long-term cognitive and behavioural deficits. Published July 23 2022
10,000,000 / year worldwide
The fundamental injury means the brain matrix is disrupted, What happens at the cellular level is destruction of synaptic connections, axonal and dendritic damage leaving debri and a neuro-inflamatory cascade within the glial tissue.
When a TBI occurs, the initial injury can disrupt the BBB, which triggers a cascade of cell death, torn, disrupted tissues and debris.The long-term injury causes inflammation and swelling, and results in the immune response to spring into action, but also can lead to an impairment of the brain’s energy sources, or can choke off the brain’s blood supply, leading to more neuronal cell death and permanent disability.
Concussion can last a lifetime, There is a 70% reoccurrence rate.
Short period - Post concussion Syndrome, some initial recovery however 90% of adults have at least a few symptoms of Post Concussive Syndrome
Involving cognition, - memory, calculations, logic, understanding concepts
Emotional control, - inappropriate reactions, anger frustration, poor control
Balance and Coordination - clumsy, accident prone, fearful , anxious (40%)
Recall Muhammad Ali - pugitatitive dementia (Parkinsonism)
Concussion in sport is now controversial, class actions are common place.
Ocula can be used in two common ways
1. On the field. Compare either baseline or normative database.
2. In the clinic. Used for pre and post assessment of treatment.
The eyes connect either directly or indirectly to every part of the brain.
There are 4 types of eye movements, vergence, Vestibulo ocular movements, saccades and pursuits.
Ocula measures pupillary dynamics in relation to the Pupillary Light Reflex.
The PLR is very complex.
Light - retina - nuclei - muscle constriction/dilation
Many brain bits influence the final result.
The ANS, Sympathetic Vs Parasympathetic - push/pull modulation
Symp - open the pupil
Parasymp - constrict the pupil
Pupils are the most accurate representation of the current state of the ANS
other systems are cardiac regulation (HRV), gut motility and organs that secrete stuff.
Concussion disrupts large amounts of brain architecture. Destroying the synaptic junctions especially the newer connections before they have become reinforced by habituation.
Latency will be affected - 100ms to process, 100ms to move the eye
Cortical damage can affect the eye fields in the frontal lobe where executive functioning occurs . - Poor decisions, foggy head, confused,
Eye fields in the parietal lobe(most active part of the neocortex) where spacial awareness takes place. - poor coordination, disorientation,
Supplementary eye field of the frontal premotor area or the Cingulate eye field where emotional salience occurs, - inappropriate behaviour, crying excessively, distressed
Brain stem damage can involve many parts.
When it’s the Superior Colliculus, either it’s afferent or efferent connections - saccades become inaccurate - with diverse consequences.
With Dysautonomia expect - glucose dysregulation, cardiac dysfunction, gut problems etc
Pupillary metrics:
Constriction Time and speed are parasympathetic reactions
Too slow -the parasympathetic system is sluggish or the
Sympathetic’s won’t release
or likewise
if Constriction is too Fast, either Parasymp is overactive or Sympathetics are holding the Parasympathetics from acting properly.
Concussion slows the Constriction and the Dilation.
Dilation is the job of the sympthetics - the reverse of the above.
Which is which - correlate with other signs and symptoms eg BP, HR, Resp Rate, Capillary flushing,
Pupillary Diameter is the sum total of all influences but predominately determined by the Cortex and Brain Stem. The light on the retina initiates a reaction but the result is a complex mixture of many influences.
Concussion decreases the range of Min to Max pupillary diameter.
Great for tracking progress.
Recovery Time again is the result of how healthy the system is. Too slow is bad, Fast is good. usually.
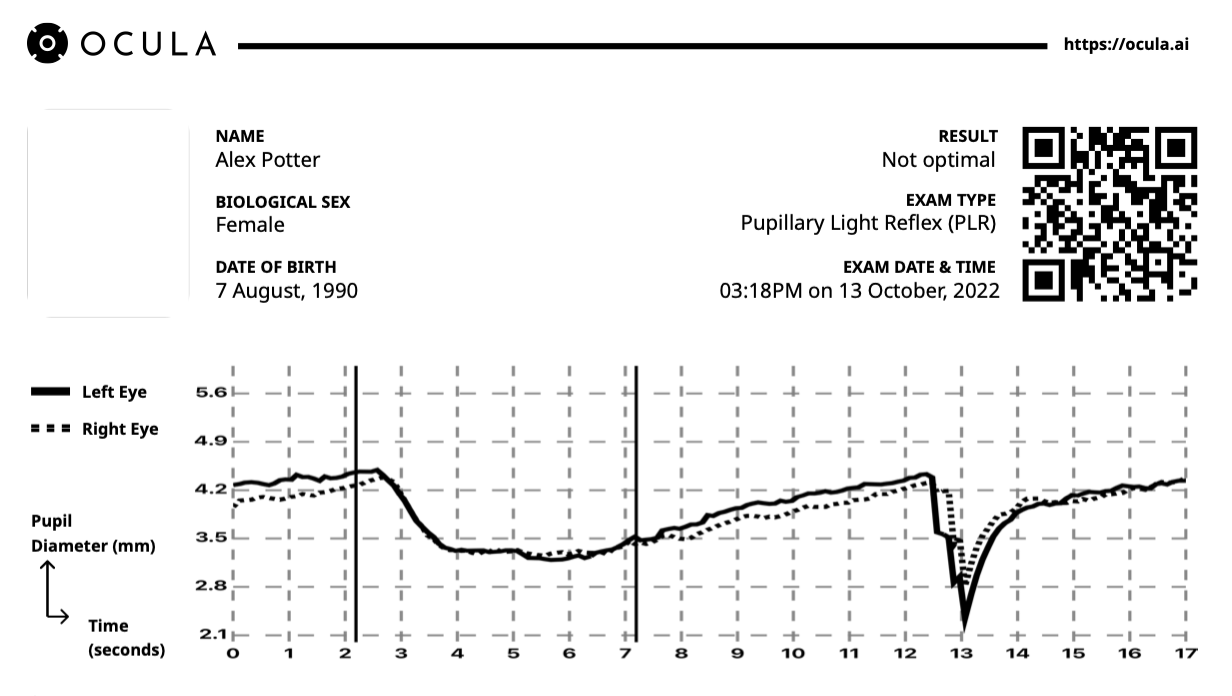
This is an example of a very mild post concussive brain injury.
The latency is too slow, as is the constriction velocity. The recovery time is good and the ‘holding’ ability of the brain to maintain the pupil constricted is good. Both eyes are similar and the range of pupillary movement is ok. The dip at !3secs is a blink artifact.
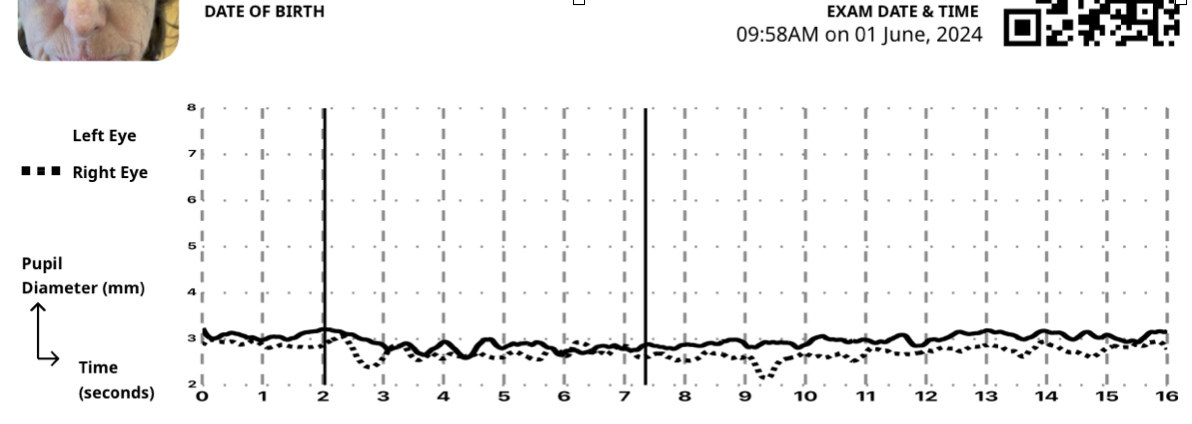
This presentation is common is also common in chronic illness.
Above is a severe concussion (class 3) of 3.5 mo duration. Note this patient’s nervous system is largely unresponsive to the light stimulus.